Extrusion process is used for manufacturing long and straight metal parts. The shape of the cross-sections can be solid round, rectangular, to T shapes, L shapes and Tubes etc. Extrusion is done by squeezing the metal in a die by using a mechanical or hydraulic press.
Extrusion is capable of producing compressive and shear forces in the stock material. As tensile is not produced, this makes very high deformity a possibility without actually tearing the metal. A wear resistant material lines the cavity in which the raw material is contained . This helps to resist the high radial loads as the material is pushed into the die.
Features of Extrusion Process:- Cost effective: Minimizes the need for secondary machining process.
- Surface finish: For steel is 3 µm; (125 µ in), for Aluminum and Magnesium -0.8 µm (30 µ in).
- Cross-section: Wide variety of cross-sections can be made.
- Minimum thickness: For steel 3 mm (0.120 in), for Aluminum and Magnesium 1mm (0.040 in).
- Minimum cross section: For steel 250 mm (0.4 in) for steel.
- Corner and fillet radii: 0.4 mm (0.015 in) for Aluminum and Magnesium, for steel the minimum corner radius is 0.8mm (0.030 in) and 4 mm (0.120 in) fillet radius.
An example of Hot Extrusion Process using Aluminium Alloy is briefly described here:
The alloyed press bars are cut into smaller pieces and heated up in an induction furnace to 450ñ500°C. The bar is then pressed with very high force using speeds between 5ñ50 m/min through a hollowed tool. As a result a profile is formed. The length of the profile ranges between 25ñ45 m. Immediately after the pressing operation, profile is cooled with air or water.
The profile is straightened and internal stresses released by stretching it in a pulling machine just after cooling. The profile is then cut into required lengths. Finally ageing gives the strength of the material. Which can be done by natural ageing at normal temperature or artificial ageing done at elevated temperature of 170ñ185°C.
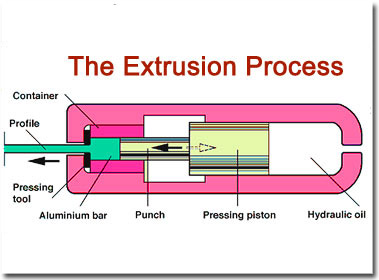
Application of Extrusion Process: Trim parts as used in automobile and construction equipment, railings, window frame members, structural parts etc.
Extrusion can be of two types Hot ExtrusionGenerally done at fairly high temperatures, approximately at 50 to 75 % of the melting point of the metal. The pressures range from 35-700 MPa (5076 - 101,525 psi). To cool down the high temperatures and pressures and its adverse effect on the die life as well as other components, good lubrication is a must. Oil graphite and glass powder is preferred as lubricants.
Application of Hot Extrusion:Aluminium, copper with their alloys are successfully used to manufacture products using hot extrusion process. Electrical wires, bars and tubes are some of the items produced.
Cold ExtrusionCold extrusion takes place at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures. This process is useful for withstanding the stresses created by extrusion.
The advantages of cold extrusion are:- No oxidation process .
- Good mechanical properties provided the temperatures created are below the re-crystallization temperature. Good surface finish
Application of Cold Extrusion:
Examples of the metals that can be extruded are copper, lead, tin, aluminum alloys, titanium, molybdenum, vanadium, steel. Which are used to make parts like collapsible tubes, gear blanks, aluminum cans, cylinders etc.
In automobile sector they have found wide applications in Injection technology; Engine control; Fuel supply; Automatic transmissions Seat technology; Safety systems (restraint systems).
